
In the dynamic world of construction financing, understanding the intricate relationship between economic conditions and construction loan interest rates is essential for both builders and investors. As the economy ebbs and flows, various factors such as inflation, employment rates, and GDP can directly influence how much it costs to secure funding for a new project.
This article delves into the key economic indicators that shape interest rate trends, providing insights into historical data and current market behavior. By analyzing how these factors interact in different economic environments, we will explore the implications for borrowers and lenders alike. Additionally, we’ll offer predictions on future trends, empowering you to make informed decisions in an ever-evolving landscape. Join us as we navigate the complexities of construction loan interest rates under varying economic conditions.
Understanding Economic Conditions Affecting Construction Loans
Economic conditions play a crucial role in shaping the landscape of construction loan interest rates. When discussing how economic factors influence these rates, it is essential to recognize several key elements:
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP): A growing economy typically indicates a healthy construction market, leading to increased demand for loans and potentially higher interest rates. Conversely, during economic downturns, construction activity diminishes, which can lower interest rates.
- Inflation Rates: Rising inflation often leads to higher interest rates as lenders increase rates to maintain their profit margins. Conversely, stable or low inflation can encourage lower construction loan rates, making borrowing more attractive for developers.
- Employment Rates: Higher employment rates usually correlate with increased consumer confidence and spending, contributing to a booming construction sector. This can drive up demand for loans, consequently raising interest rates.
- Monetary Policy: Central banks influence interest rates through monetary policy. When central banks raise benchmark rates to curb inflation, construction loan rates often follow suit. Understanding the central bank’s stance can help predict shifts in loan rates.
- Supply Chain Conditions: Economic disruptions affecting the supply chain can impact construction costs and timelines. As construction becomes more expensive or delayed, this may lead lenders to adjust interest rates based on perceived risks.
how economic conditions shape construction loan interest rates is a complex interplay of various factors, including GDP, inflation, employment levels, monetary policy, and supply chain dynamics. Keeping an eye on these indicators can provide insights for both borrowers and lenders in the construction financing market.
How Economic Indicators Impact Interest Rate Trends
The relationship between economic indicators and interest rate trends is complex yet crucial for understanding how construction loan rates shift over time. Various economic factors provide insight into the broader financial landscape, directly influencing the cost of borrowing for construction projects.
How economic growth is a primary indicator that banks and lenders use to gauge future interest rates. When the economy is expanding, demand for loans increases, which can lead to higher interest rates. Conversely, during economic downturns, the demand for loans typically declines, reducing interest rates as lenders compete to attract borrowers.
Inflation is another key economic indicator that affects interest rates. As inflation rises, lenders may increase rates to maintain their profit margins, as the purchasing power of the money they receive back in the future will be lower. Therefore, monitoring inflation trends is essential for anticipating changes in construction loan interest rates.
Unemployment rates also play a significant role. High unemployment often signals economic weakness, leading to lower interest rates as lenders seek to stimulate borrowing. In contrast, low unemployment can indicate a robust economy, where increased demand for loans can push interest rates higher.
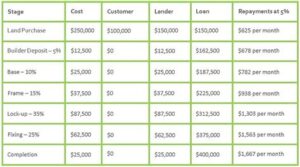
The central bank’s monetary policy, particularly actions taken by the Federal Reserve in the United States, has a profound impact on interest rates. By adjusting the federal funds rate, the Fed influences overall borrowing costs across the economy, directly affecting construction loan rates. A lower federal funds rate generally makes borrowing cheaper, whereas an increase can lead to higher rates.
Other financial indicators, such as consumer spending and housing market trends, provide additional context for predicting interest rate movements. A thriving housing market may suggest higher construction loan activity, prompting lenders to adjust their rates accordingly.
Understanding how economic indicators interact with interest rates can empower borrowers and investors in the construction industry to make informed financial decisions, maximizing their opportunities while minimizing risks.
Analyzing Historical Data: Economic Conditions and Loan Rates
When examining the relationship between economic conditions and construction loan interest rates, historical data plays an essential role. By analyzing past interest rate trends alongside significant economic events, we can decipher how how economic fluctuations impact lending rates over time. This analysis not only provides insights into the past but also helps predict future trends in the construction loan market.
Throughout history, periods of economic expansion generally correlate with lower interest rates as lenders look to stimulate growth through increased lending. Conversely, in times of economic downturn or uncertainty, interest rates often rise as lenders become more risk-averse. For instance, during the 2008 financial crisis, we witnessed a dramatic spike in construction loan rates due to increased risk and a decrease in demand for new projects.
Another interesting trend is the impact of inflation on construction loan rates. Historical data reveals that during periods of rising inflation, such as the late 1970s, interest rates surged as lenders sought to protect their investments from eroding purchasing power. This phenomenon has repeated itself in various economic cycles, highlighting the crucial role inflation plays in determining loan costs.
Moreover, government policies and regulatory changes can significantly affect the loan landscape. The introduction of quantitative easing measures by central banks during economic crises has lowered interest rates in many instances, providing a temporary reprieve for borrowers. Historical analysis shows that such measures can result in a boom in construction loans as capital becomes more accessible.
By studying historical data surrounding economic conditions and construction loan rates, we can identify patterns and trends that inform our understanding of the current lending environment. Such analysis is vital for borrowers and lenders alike, as it provides a clearer picture of what to expect in the future of construction financing.
Factors Influencing Construction Loan Rates in Various Economies
Construction loan interest rates are affected by a multitude of factors that vary from economy to economy. Understanding these factors can help borrowers make informed decisions and manage their financing effectively. Below are some key influences on construction loan rates:
- Economic Stability: Countries with stable economic environments usually offer lower construction loan rates. In contrast, economies facing volatility often see increased rates due to higher perceived risks by lenders.
- Inflation Rates: Higher inflation typically leads to increased interest rates as lenders seek to maintain their profit margins amid rising costs. Conversely, lower inflation can encourage more favorable lending rates.
- Central Bank Policies: The policies set by central banks, including benchmark interest rates and monetary policy strategies, significantly influence construction loan rates. A more accommodative central bank policy can result in lower loan rates.
- Demand for Construction: In economies experiencing robust growth and high demand for new construction projects, lenders may raise rates due to increased competition for capital. On the other hand, a downturn can result in increased availability of funds and lower rates.
- Credit Risk Assessment: The creditworthiness of borrowers and the perceived risk associated with lending in particular economies can affect rates. Higher default risks usually lead to higher interest rates.
- Local Regulations: Regulatory frameworks and building permits can influence construction costs and, consequently, the rates at which loans are issued. Stricter regulations may drive costs up, impacting loan rates.
- Global Economic Influence: Economic conditions in major economies can have ripple effects on local markets. For instance, instability in a major economy can lead to tighter borrowing conditions globally, affecting local construction loan rates.
- Supply Chain Issues: In times of supply chain disruptions, costs of materials can skyrocket, which may lead lenders to adjust their rates in response to the increased financing needs of borrowers.
- Real Estate Market Trends: The health of the real estate market, including property values and demand, directly impacts construction loan rates. Rising property values may lead to higher loan amounts and, subsequently, different rate structures.
Understanding the various factors that influence construction loan rates in different economies is crucial for anyone looking to secure financing for construction projects. By keeping abreast of these conditions, borrowers can better navigate their financing options.
Predictions for Construction Loan Interest Rates Based on Economic Changes
As we analyze the current how economic conditions shape the financial landscape, it’s essential to consider how they will influence construction loan interest rates in the near future. Various economic indicators provide a roadmap for predicting these trends, and by understanding them, borrowers can better position themselves.
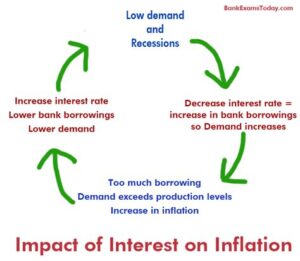
The first factor to consider is inflation rates. Historically, when inflation rises, central banks may increase interest rates to maintain economic stability. This could lead to higher construction loan rates as lenders adjust to the increased cost of borrowing. Similarly, if the economy experiences a downturn, construction loan interest rates might decrease as lenders become more competitive in a struggling market.
Another critical factor is employment rates. A healthy job market typically leads to increased demand for new construction as people seek to buy homes. This heightened demand can drive interest rates up. Conversely, during periods of high unemployment, the demand for construction loans may decline, leading to reduced interest rates as lenders attempt to attract borrowers.
Moreover, government policies play a significant role in shaping interest rates. Tax incentives for real estate development or infrastructure spending can stimulate the construction industry, impacting loan rates positively. In contrast, regulations that restrict lending practices may tighten the availability of construction loans, resulting in higher interest rates.
Global economic conditions, such as trade relationships and geopolitical stability, can also affect construction loan rates. For instance, uncertainties in international markets may lead to fluctuations in interest rates, impacting the cost of borrowing for construction projects.
Predicting construction loan interest rates requires a thorough understanding of ongoing how economic changes, as various factors interplay to shape the financial prospects for borrowers. Staying informed about these economic shifts can provide essential insights for both lenders and borrowers looking to navigate the construction loan landscape effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do economic conditions affect interest rates for construction loans?
Economic conditions directly influence interest rates due to changes in supply and demand for credit. When the economy is strong, demand for loans increases, which typically drives interest rates higher. Conversely, during economic downturns, demand may decrease, leading to lower interest rates.
What specific economic indicators influence construction loan interest rates?
Key economic indicators include inflation rates, unemployment rates, the Federal Reserve’s monetary policy, GDP growth, and housing market trends. For instance, rising inflation can lead to higher interest rates as lenders seek to maintain their profit margins.
How does inflation impact construction loan interest rates?
Inflation generally leads to higher interest rates because lenders must compensate for the decreased purchasing power of future loan repayments. As inflation rises, lenders increase rates to maintain returns.
What role does the Federal Reserve play in determining construction loan interest rates?
The Federal Reserve influences construction loan interest rates by setting the federal funds rate, which affects the cost of borrowing money for banks. Changes in this rate can subsequently impact the interest rates offered on construction loans.
Are construction loan interest rates the same across different regions?
No, construction loan interest rates can vary significantly by region due to local economic conditions, property values, demand for housing, and the competitive landscape among lenders.
How can borrowers secure lower interest rates on construction loans?
Borrowers can secure lower interest rates by improving their credit scores, providing substantial down payments, choosing shorter loan terms, and shopping around for the best rates from different lenders.
Why is it important for builders to monitor economic conditions?
It’s important for builders to monitor economic conditions as they directly affect financing costs, project feasibility, and overall profitability. Understanding these conditions can help builders make informed decisions and adjust their strategies accordingly.

Leave a Reply